The role of OEE in manufacturing efficiency
In modern manufacturing, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) serves as a critical benchmark for measuring productivity. By evaluating availability, performance, and quality, OEE provides insights into how efficiently equipment is utilised. A low OEE score signals inefficiencies such as machine downtime, slow production rates, or high defect rates—all of which reduce throughput and increase operational costs.
One of the most significant contributors to low OEE is downtime, which can be either planned or unplanned. Planned downtime includes scheduled maintenance and changeovers, while unplanned downtime results from equipment failures, material shortages, or operator errors. Addressing downtime is essential, as an idle machine generates no value and can disrupt production schedules, impact delivery times, and reduce overall profitability.
This guide explores how manufacturers can improve OEE through better tracking, root cause analysis, and targeted interventions. Special emphasis is placed on the role of OEE tracking software, which enables real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making.
Measuring OEE accurately: The foundation for improvement
Accurate measurement is the starting point for improving OEE. Many manufacturers rely on manual data collection, which introduces errors and inconsistencies. Without a precise and automated method for tracking OEE, efforts to reduce downtime and enhance efficiency become ineffective.
OEE calculation and the role of data tracking
OEE is calculated as the product of three key metrics:
- Availability: (Run time / Planned production time) – Measures how often equipment is available for operation.

- Performance: (Ideal cycle time × Total count) / Run time – Reflects the speed at which equipment operates compared to its maximum potential.

- Quality: (Good count / Total count) – Indicates the percentage of defect-free products.

The reliability of these calculations depends on the quality of the input data. OEE tracking software automates data collection, eliminating errors associated with manual logging and ensuring real-time visibility into production losses. By integrating OEE tracking software with production lines, manufacturers gain a continuous flow of accurate performance data, allowing for immediate intervention when issues arise.
Reducing Downtime and Improving Availability

Availability losses are among the most significant contributors to poor OEE. These losses occur when equipment is scheduled for production but is not operating. The Six Big Losses in Manufacturing identify two primary causes of availability losses:
- Unplanned downtime: Machine failures, breakdowns, and other unexpected stoppages.
- Setup and adjustment losses: Time lost due to changeovers, maintenance, and machine adjustments.
Minimising unexpected equipment failures
Unplanned downtime due to equipment failure can have a cascading effect on production efficiency. Without a structured approach to maintenance, manufacturers experience frequent breakdowns, emergency repairs, and inconsistent production output. Implementing predictive and preventive maintenance strategies is crucial.
- Predictive maintenance: Uses real-time monitoring and analytics to detect early signs of equipment deterioration. Sensors collect data on vibration, temperature, and other parameters to identify potential failures before they occur.
- Preventive maintenance: Involves regular servicing and inspections based on historical failure patterns. While less data-driven than predictive maintenance, it ensures that critical components are replaced before they lead to breakdowns.
Optimising changeovers and setup time
Changeover losses are another significant contributor to downtime. The Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) methodology helps manufacturers reduce setup times by streamlining changeover processes. Key steps include:
- Standardising procedures to ensure consistency across operators and shifts.
- Separating internal and external setup tasks, so preparatory steps occur while the machine is still running.
- Using quick-change tooling and automation where possible to reduce manual adjustments.
Reducing setup and adjustment time increases availability and ensures that more of the scheduled production time is used for actual manufacturing.
Enhancing performance by addressing speed losses
Even when machines are operational, they may not run at optimal speeds. Performance losses occur due to small stops, slow cycles, and inefficiencies in production flow. The Six Big Losses framework highlights two major performance losses:
- Idling and minor stops: Short, frequent interruptions caused by misfeeds, jams, or sensor issues.
- Reduced speed: Operating below the ideal cycle time due to mechanical wear, improper settings, or poor material quality.
Identifying and eliminating minor stops
Minor stops often go unnoticed because they are brief, but they accumulate over time. The best way to tackle these losses is through real-time monitoring. Manufacturers can use:
- OEE tracking software to log every instance of a minor stop and identify patterns.
- Autonomous maintenance programs, where operators are trained to resolve common issues before they escalate.
- Standardised problem-solving techniques like root cause analysis to determine why minor stops occur.
Optimising cycle times and machine speed
Reduced speed losses occur when machines operate below their design speed due to suboptimal machine settings, insufficient lubrication, or worn-out components. Solutions include:
- Real-time performance tracking to detect slowdowns as they happen.
- Operator training on optimal machine speeds and process standardisation.
- Upgrading outdated equipment or recalibrating machinery to restore efficiency.
Addressing speed losses ensures that equipment operates at peak efficiency, contributing to higher overall productivity.
Improving quality by minimising defects and rework
Quality losses occur when products fail to meet specifications, leading to scrap, rework, and wasted production time. The Six Big Losses framework categorises these as:
- Production defects: Flaws that occur during regular operation.
- Startup rejects: Defects that arise after changeovers or machine warm-ups.
Early detection of quality issues
Quality problems often go unnoticed until final inspections, leading to high scrap rates. Preventive measures include:
- Automated quality checks at multiple production stages to identify defects early.
- Statistical process control (SPC) to track variation in production output.
- Root cause analysis on recurring defects to implement long-term corrective actions.
Standardising processes and providing operators with clear guidelines help reduce quality fluctuations, ensuring a higher percentage of defect-free products.

Why MaintMaster OEE stands out as an OEE tracking software
A key enabler of OEE improvement is OEE tracking software, which automates data collection, provides real-time visibility, and enables manufacturers to make informed decisions. MaintMaster OEE is an advanced solution that offers:
- Real-time OEE monitoring to detect losses instantly.
- Pareto analysis of downtime causes, allowing targeted interventions.
- Seamless integration with CMMS systems like MaintMaster for predictive maintenance.
- Automated alerts and notifications to address production issues proactively.
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics for continuous improvement.
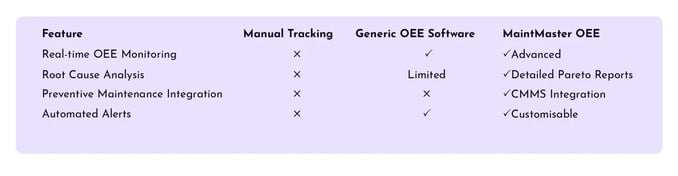
By leveraging MaintMasters OEE’s advanced tracking capabilities, manufacturers can shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive efficiency improvement, ensuring sustainable gains in OEE and downtime reduction.
A data-driven approach to OEE improvement
Improving OEE and reducing downtime requires a structured, data-driven approach. By accurately measuring OEE, addressing the Six Big Losses in Manufacturing, and leveraging OEE tracking software, manufacturers can significantly enhance efficiency.
Key takeaways include:
- Reducing downtime through predictive maintenance and optimised changeovers.
- Enhancing performance by eliminating minor stops and improving machine speed.
- Improving quality through early defect detection and process standardisation.
By integrating real-time tracking solutions like MaintMaster OEE, manufacturers gain the insights needed to drive continuous improvement, maximise productivity, and maintain a competitive edge.

