Chapter 4
KPI for breakdown analysis
Breakdown analysis KPI is a measure of the frequency and impact of equipment failures and breakdowns. It helps organisations understand the root causes of breakdowns and identify opportunities for improvement in their maintenance practices and equipment reliability.
Theese are the most important breakdown analysis that you need to track:
- Immidiate corrective maintenance ration
- MTBF – (MOTBF)
Mean (Operating) Time Between Failures - Top 5 site-objects
Top 5 site-objects with the most jobs / highest costs / most reported time - Breakdown hours
Objects with the most downtime caused by breakdowns.
By tracking and analysing these and breakdown analysis KPIs, organisations can identify trends and areas for improvement in their maintenance practices and equipment reliability. This will help you optimise maintenance resources, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment performance.
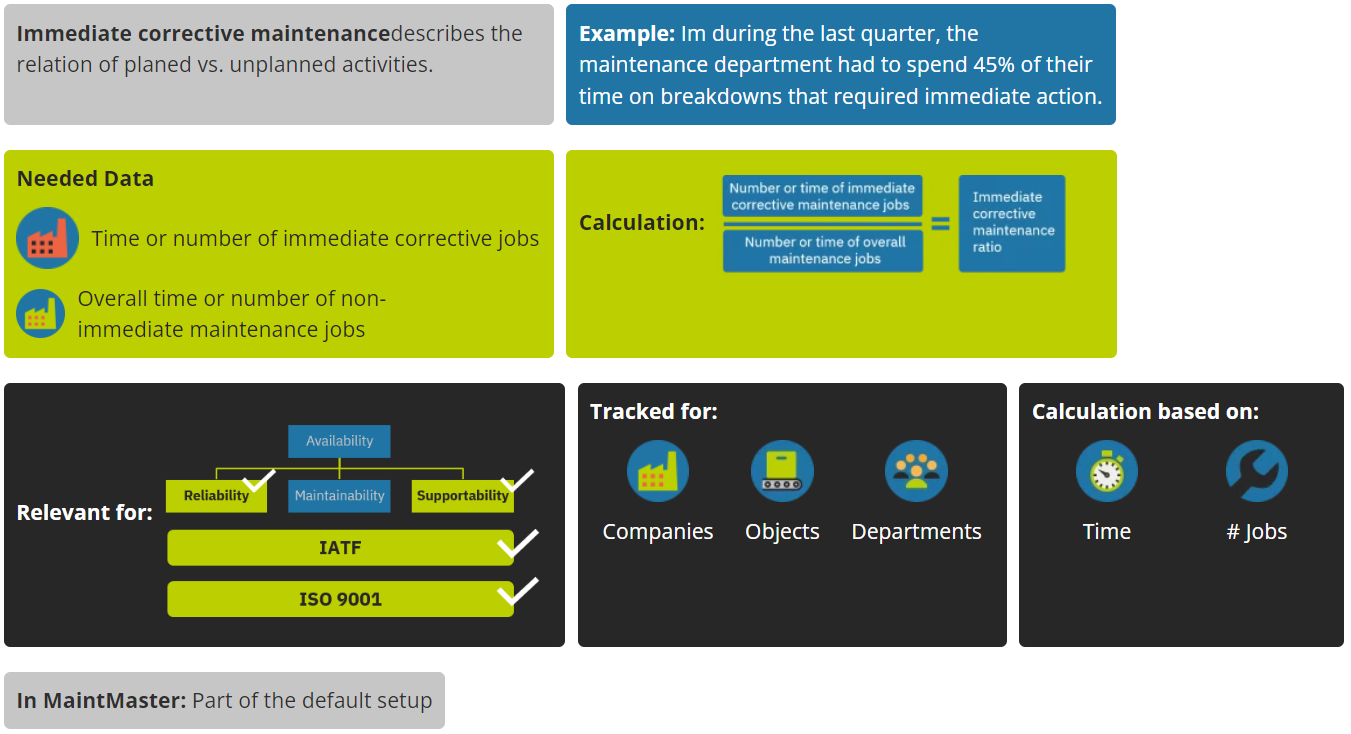
Immediate corrective maintenance ratio
How much immediate corrective maintenance is done in relation to all other maintenance activities?
Immediate Corrective Maintenance Ratio is a measure of the amount of immediate corrective maintenance (also known as breakdown maintenance) that is performed in relation to all other maintenance activities. Immediate corrective maintenance is maintenance that is carried out as soon as possible after a breakdown or malfunction has occurred, with the goal of getting the equipment back up and running as quickly as possible.
A high Immediate Corrective Maintenance Ratio may indicate a high frequency of equipment failures and breakdowns, which could be caused by a variety of factors such as poor equipment design, inadequate preventive maintenance, or a lack of spare parts. On the other hand, a low Immediate Corrective Maintenance Ratio may indicate that equipment is generally reliable and requires fewer breakdown repairs.
By tracking the Immediate Corrective Maintenance Ratio over time, organisations can identify trends and areas for improvement in their maintenance practices and equipment reliability. This can help them optimise maintenance resources, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment performance.
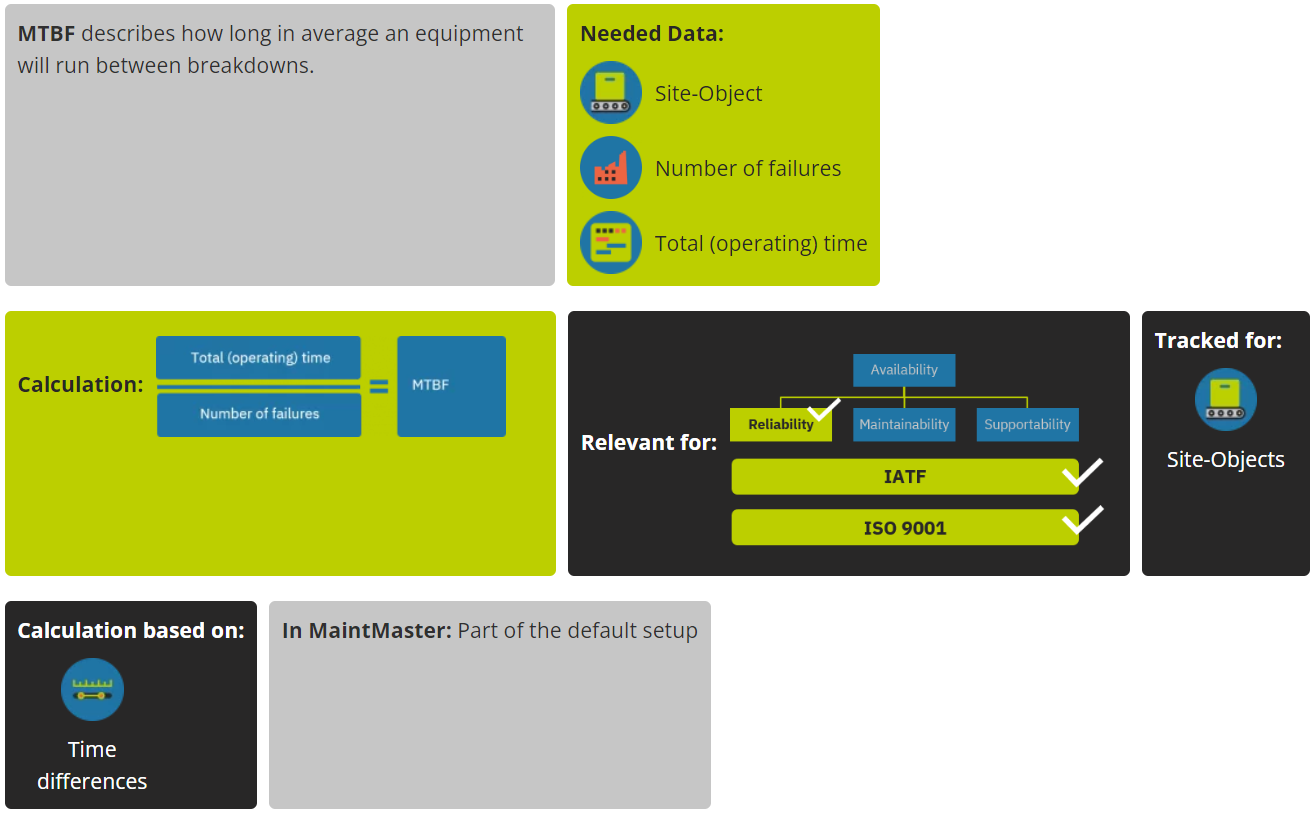
MTBF – (MOTBF)
Mean (Operating) Time Between Failures
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a measure of the average time that a piece of equipment operates without failing or experiencing a breakdown. It is calculated by dividing the total operating time of the equipment by the number of failures that have occurred.
MTBF is an important metric for organisations that rely on equipment to meet production goals and customer demand. A high MTBF indicates that the equipment is reliable and requires less maintenance, while a low MTBF may indicate that the equipment is prone to failures and breakdowns.
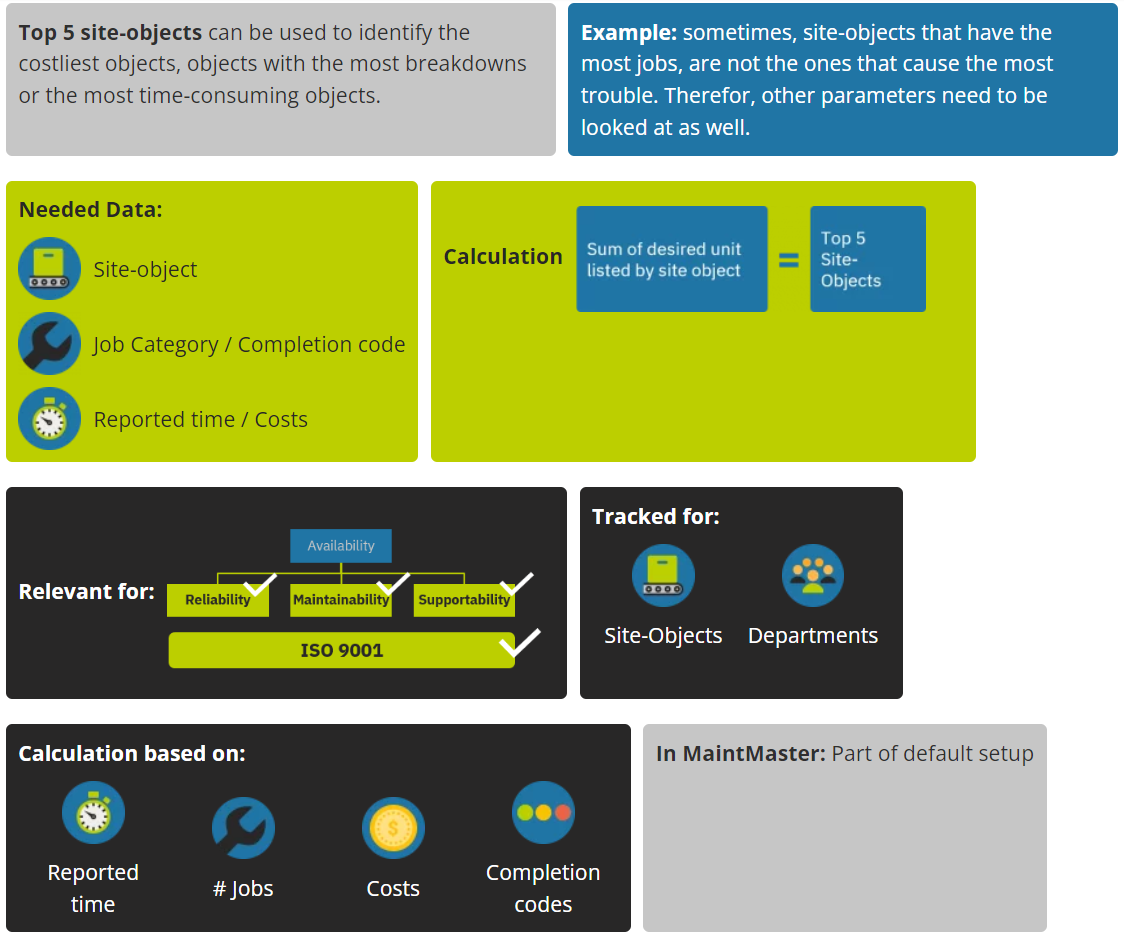
TOP 5 Site -Objects
Top 5 site-objects with the most jobs / highest costs / most reported time…
𝗧𝗼𝗽 𝟱 𝗢𝗯𝗷𝗲𝗰𝘁𝘀 with the most unplanned stops is one of the most important KPI to look at. If we don’t measure which objects have the most breakdowns, there will be a lot of talk in production on what to improve but all of these initiatives will not be based on facts. We can be even more precise in our measurement by starting to count the time that machine is in a downstate. Tracking the amount of unplanned stops in combination with breakdown hours will give you a clear picture on what to improve. This KPI is highly dependent on operators and production personal reporting unplanned stops in a proper manner. Therefore we recommend to report back to them what improvements have been made based on their data. This way, they will understand that each time they fill in a fault report, they actually create valuable information for the maintenance department to improve the reliability of their equipment.
Breakdown hours
Objects with the most downtime caused by breakdowns.
One of the most effective ways to measure the reliability of your equipment is to measure its downtime. This is so important that there are often systems in place that measure downtime outside the maintenance software. If you have both an automated system in place to monitor machine downtime as well as maintenance reported downtime, you may find that the values in both systems vary a lot.
That is because: -> It may take a while for production to report an error -> It may need some time after the repair is done for the machine to start up again If your monitoring system is not able to differentiate between breakdown hours and other causes for the machine to stand still, you may get additional differences because of: -> Missing materials -> Insufficient staffing of operators -> Break time for operators Therefore, having both systems in place may provide useful information both for the maintenance department as well as production.
By looking at differences in maintenance reported downtime and machine monitoring, we can get clues on how the operators can improve their processes as well as us, the maintenance team.

Maintmaster KPI Manual
Improve your maintenance strategy by using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track and optimise your operations. Download our comprehensive manual to get started.
