Chapter 6
KPI for restoration speed
Restoration Speed KPI is a measure of the speed at which equipment is restored to normal operation after a failure or breakdown. It is an important metric for organisations that rely on equipment to meet production goals and customer demand, as a faster restoration speed can minimise downtime and improve overall equipment performance.
By tracking Restoration Speed KPI over time, organisations can identify trends and areas for improvement in their maintenance practices and equipment reliability. This will help them optimise maintenance resources, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment performance.
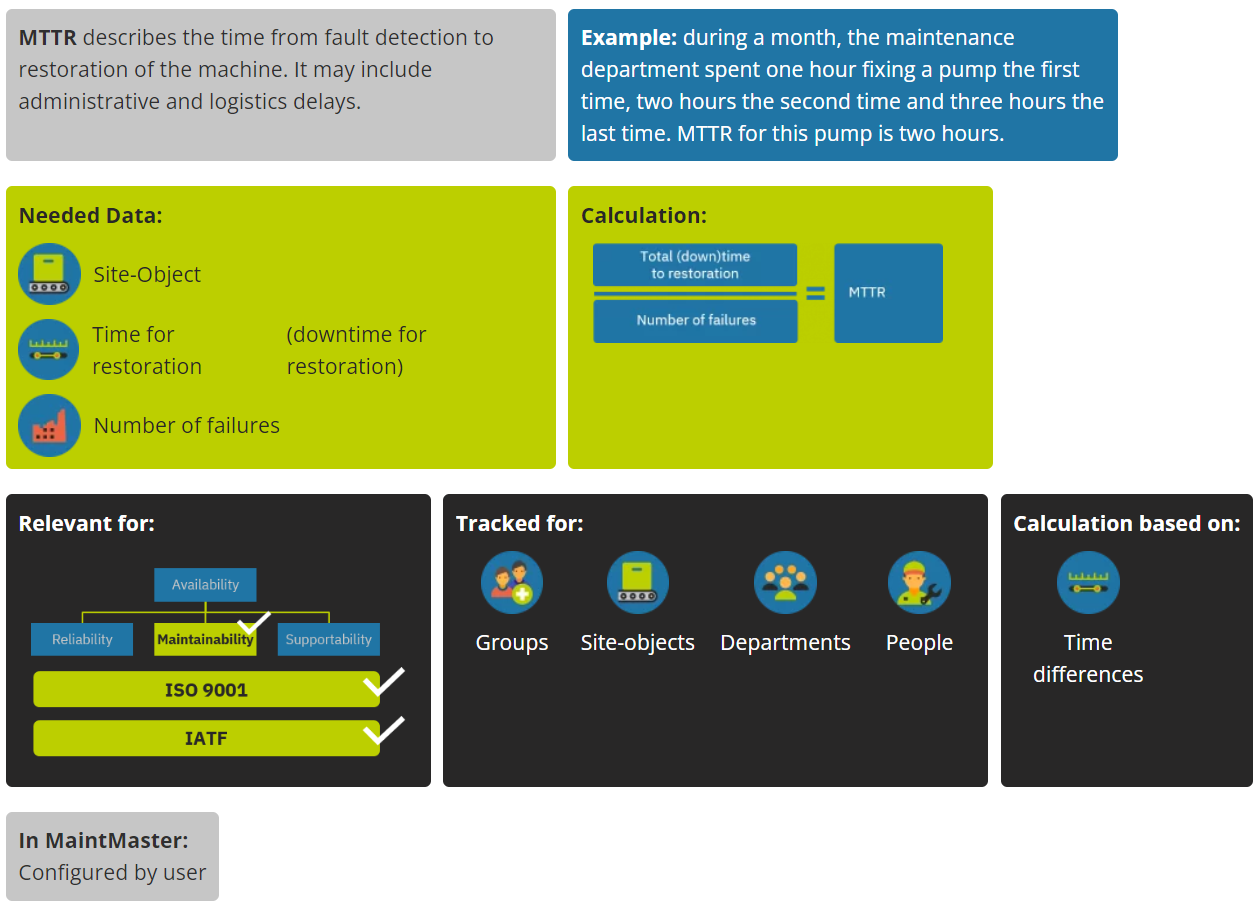
MTTR – (MDTR)
Mean Time To Restoration – (Mean Downtime To Restoration)
MTTR is a KPI which is officially recommended to be measured by several Quality Management Systems e.g. IATF 16949.
It describes the mean time from a fault detection to restoration (repair, recover) of a machine or system.
To measure it correctly you need to have a clear and described routine in place for reporting the detection of a fault and completion of the repair. The clear and documented way of measure will help you a lot during audits.
In order to have a an easy way of measuring and following up MTTR it is recommended to report ALL corrective maintenance tasks in your CMMS. In MaintMaster you are able to analyse this KPI in several dimensions: MTTR for Machines, Lines, Departments or even groups of technicians. This is helpful if you observe changes to the KPI and need to find the root cause for these changes.
As usual we recommend to concentrate not only on absolute time measures but also consider trends and developments over a time period. MaintMaster supports this by showing you the absolute number as well as trends based on historic data.
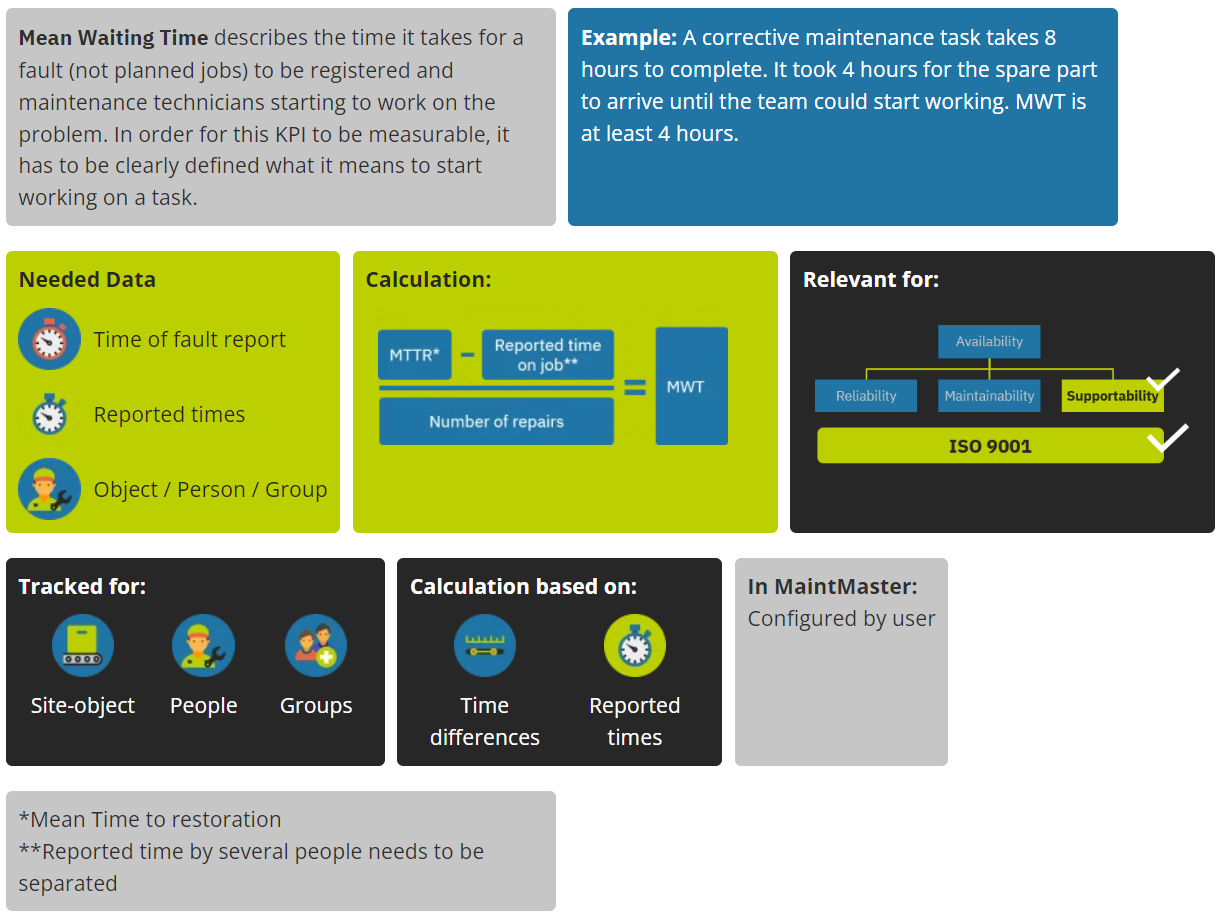
MWT
Mean Waiting Time
Mean Waiting Time (MWT) is a measure of the average time that equipment is waiting for maintenance. It is an important metric for organisations that rely on equipment to meet production goals and customer demand, as long waiting times can lead to decreased productivity and increased downtime.
By tracking MWT over time, organisations can identify trends and areas for improvement in their maintenance practices and equipment reliability. This will help them optimise maintenance resources, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment performance.
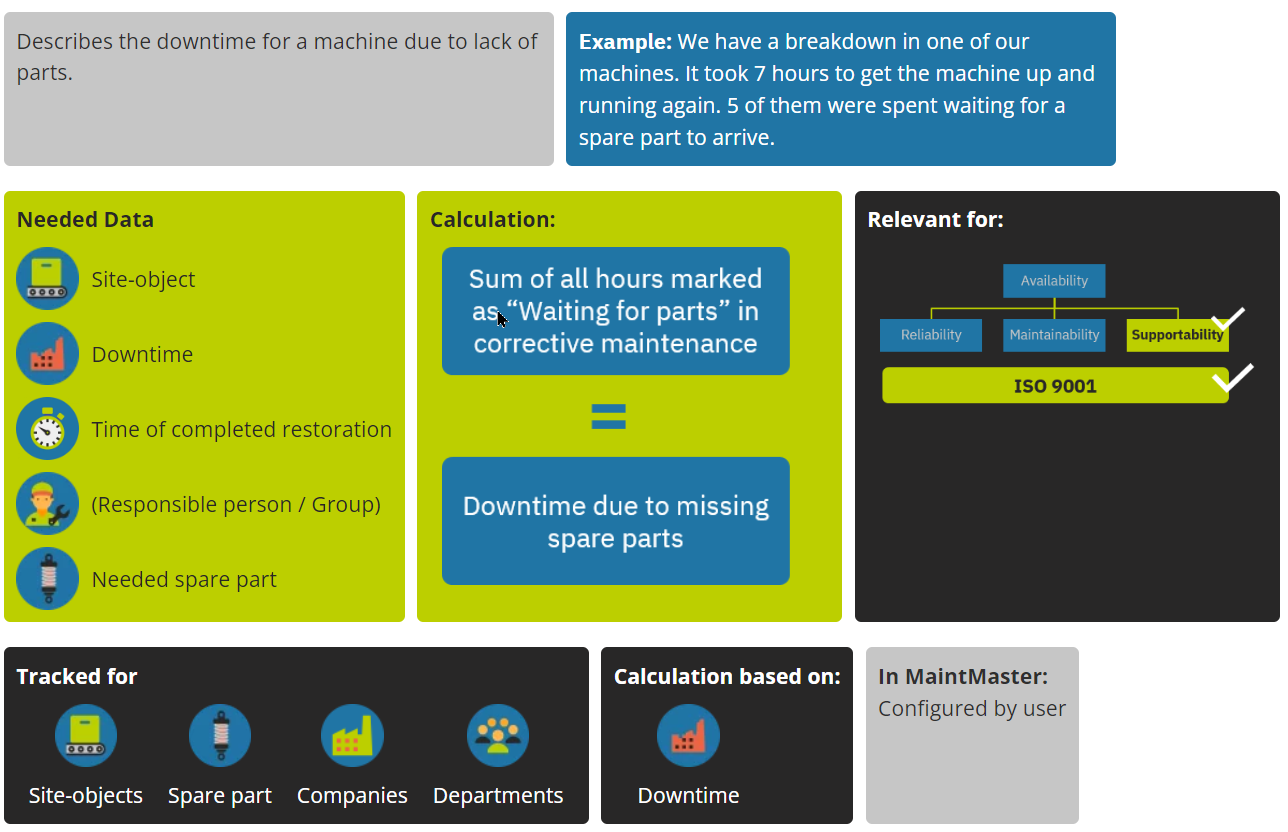
Downtite due to missing spare parts
Hours of downtime caused by missing spare parts
Downtime caused by missing spare parts is a measure of the hours of downtime caused by the unavailability of spare parts needed for maintenance or repair activities. This is a critical metric for organisations that rely on equipment to meet production goals and customer demand, as extended downtime periods can lead to decreased productivity and increased costs.
By tracking downtime caused by missing spare parts over time, organisations can identify trends and areas for improvement in their spare part management practices. This will help organisations optimise inventory levels, reduce lead times, and improve forecasting accuracy, ultimately resulting in reduced downtime and improved equipment performance.
Maintmaster KPI Manual
Improve your maintenance strategy by using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track and optimise your operations. Download our comprehensive manual to get started.
