Chapter 5
Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is maintenance carried out after a malfunction has been detected, and to bring the unit into a condition to perform the required function.
Corrective maintenance can consist of both deferred (plannable) and immediate (unplanned) corrective maintenance.
Deferred Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance which is not immediately carried out after a fault detection but is delayed in accordance
with given rules.
Immediate Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance that is carried out without delay after a fault has been detected to avoid unacceptable consequences.
Corrective Maintenance
Advantages
- Suitable for machines that are easy to replace or have a low purchase cost.
- Suitable for specific machines or parts in redundant systems where no costly side effects can be expected in case of failure.
- Requires no or limited investment in skills or technology.
Disadvantages
- Involves unforeseen breakdowns.
- Difficult and sometimes impossible to plan maintenance activities.
- Higher cost - minor machine problems go undetected and develop into costly breakdowns..
- Low or no professional development of staff.
- Higher risk for injuries in case of breakdown. Increased environmental impact.
- Higher energy consumption.
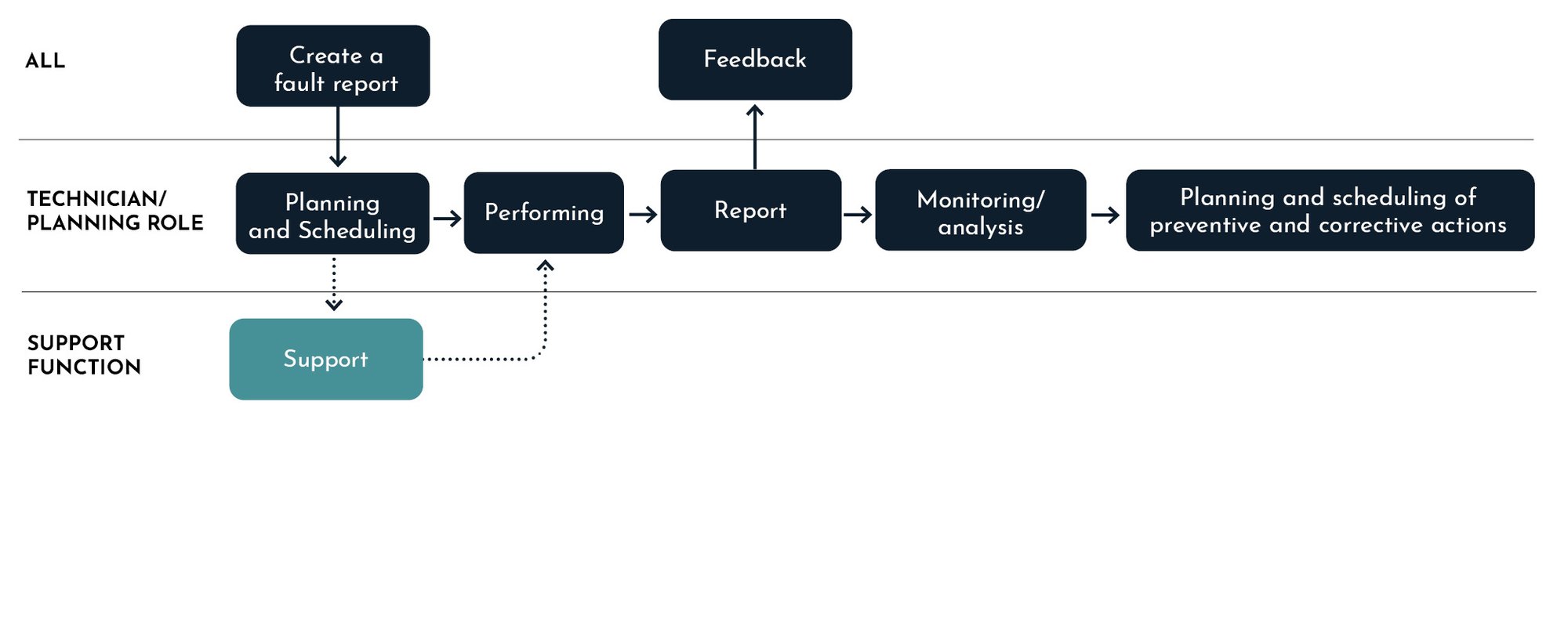
Work order flow (example)
Fault Report
To report non-urgent faults, you normally report directly into the maintenance system by clicking on the "Corrective Maintenance" button and selecting the priority of the job, as explained in the following pages. The work order is then forwarded to the maintenance department or respective area manager for further processing. In cases where the reporting person cannot, or feels uncertain, the responsible technician or manager shall assist in handling the fault report. In some organisations you report faults by phoning a dedicated person/role who creates the work order in the system. In case of a Breakdown, you always report the fault by phone before you report into the system. Reporting a fault into the system can also be done afterwards when the fault in question has been rectified, but the basic principle is that jobs should only be carried out in exceptional cases unless an order has been placed in the maintenance system.
Recipient of the fault report
The person in charge of the relevant line, area or equipment is responsible for the planning, execution and reporting of these jobs.
Completion of work orders
After completing the maintenance operation, the job must be reported immediately with the time spent and a simple analysis of the action taken to correct the problem. In the case of emergency measures using the job category "Corrective maintenance" and the completion code group "Immediate corrective maintenance", you must also state how much downtime the fault in question has caused before the job is completed in MaintMaster.
Priority levels
Priority Levels for Fault Reporting (Job Category "Corrective Maintenance")
Breakdown – The machine is at a standstill, the fault needs to be handled immediately.
Production disturbance – The machine is working but perhaps not very well.
Errors fi shortcomings – For handling deviations and things that do not directly affect operations but should be handled
Maintmaster Maintenance Manual
This free manual can be used as a practical guide and support in the daily maintenance work and as part of the introductory material for newly employed personnel.
In this manual, you will learn:
How to create vision, strategy and policies for your maintenance team
How to build a maintenance team
Which KPIs to use and how to set them up
How to base your work on the EN Maintenance Standard
And a lot more…
- 1. Maintenance according to Euorpean standards
- 2. Maintenance Vision, Strategy & Policy
- 3. Maintenance standard
- 4. Preventive Maintenance
- 5. Corrective Maintenance
- 6. Improvement Maintenance
- 7. Modification
- 8. Case Management
- 9. Organisation
- 10. Finance
- 11. Goals & Key Performance Indiscators (KPIS)
- 12. Implementation in MaintMaster
- 13. Planning & Scheduling
- 14. Spare Parts Management
- 15. LEAN - 5S
- 16. Systematic Work Environment Management
- 17. Learn the basics of a CMMS