Chapter 4
Preventive Maintenance
Effective preventive maintenance increases operational reliability, which leads to increased profitability. In the long run, it also reduces maintenance costs. We normally aim at condition-based maintenance, which is based on optimising the availability of the company's processes by anticipating the critical points in our equipment and thus preventing problems before they occur.
Cost efficiency has always to be considered. Sometimes Predictive Maintenance could be a preferred approach.
Maintenance activities that are "unnecessary" are eliminated by systematically ensuring that the work performed provides increased reliability at a lower cost. We also ensure that maintenance is a coherent entity, which includes secure access to spare parts and a functioning network of maintenance providers.
Condition-Based Maintenance
Preventive maintenance which include assessment of physical conditions, analyses and the possible ensuing
maintenance actions.
Note. The condition asessment may be by operator observation, and/or inspection, and/or testing, and/or condition monitoring of system parameters, etc., conducted according to a schedule, on request or continuous.
Predetermined Maintenance
Preventive maintenance, carried out in accordance with established intervals of time or number of units of use,
without previous condition investigation.
Note. Intervals of times or number of unit of use may be established from knowledge of the failure mechanisms of the item.
Predictive Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance carried out following a forecast derived from repeated analyses, or known
characteristics and evaluation of the significant parameters of the degradation of the item.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
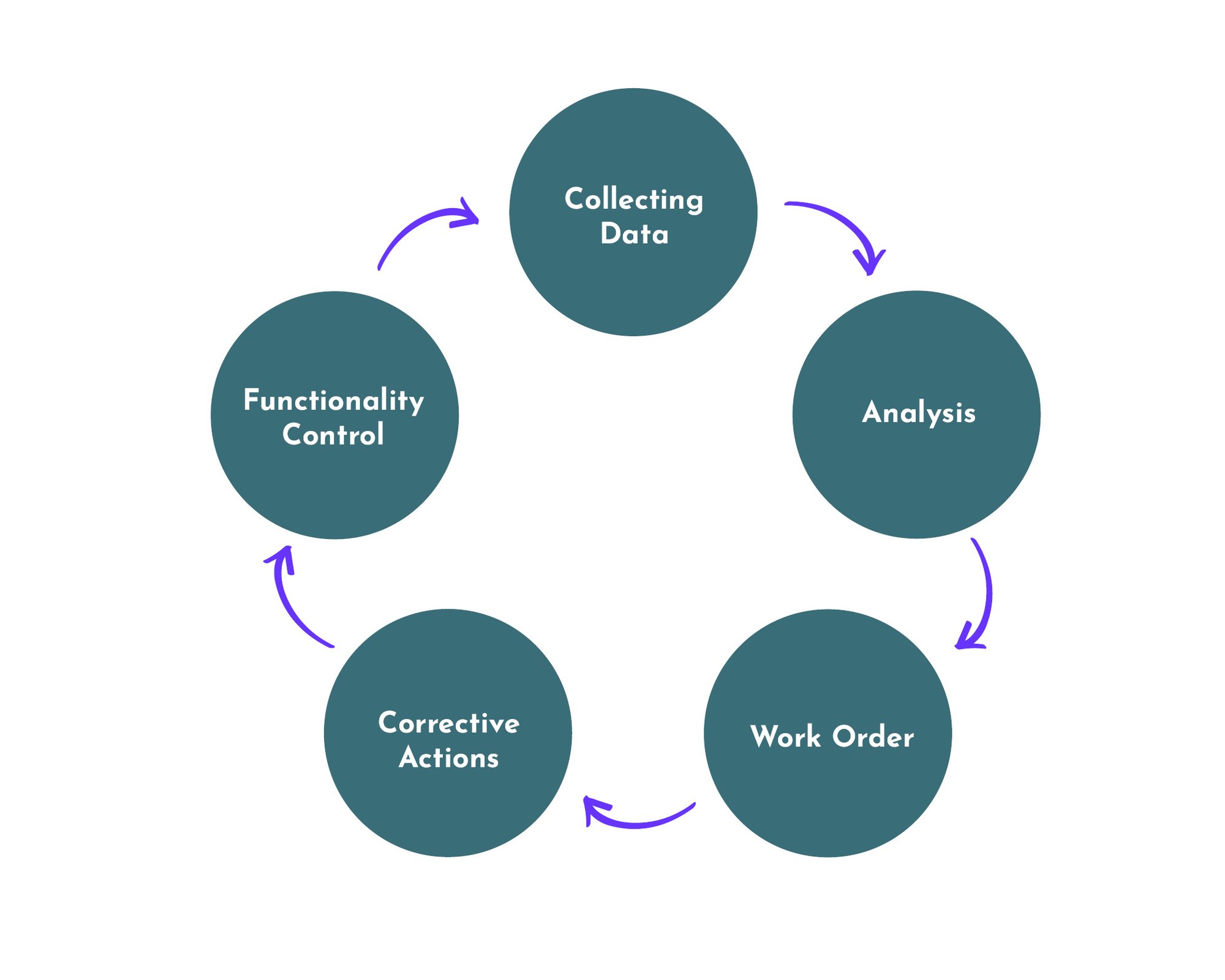
Is a methodology to acquire information on the health status of individual machines in order to identify the correct maintenance action at an optimal time. Condition-based maintenance therefore requires methods to obtain information about the health of the machine. This usually involves various measurement techniques, such as vibration measurement, thermography, ultrasonic measurement and oil analysis. The maintenance process for condition-based maintenance consists of five process steps: Collecting Data, Analysis, Work Order, Corrective actions and Functionality Control.
Advantages
- The right maintenance action at the right time.
- Planned maintenance measures instead of immediate measures.
- M;inor machine faults are detected well in time, and corrected.
- Decrease of breakdowns due to wear and tear.
- High competence development rate of maintenance staff.
- Core maintenance knowledge is built up in the organisation.
Disadvantages
- May involve high initial investment costs.
- Risk of machines beeing refurbished to early.
- Need for concept understanding and acceptance from the production.
Predetermined maintenance
Refers to preventive measures, scheduled per calendar or operating time, such as replacing oil, belts, clutch elements and other ware parts. The term also includes scheduled inspections where machines and components are dismantled for inspection.
Advantages
- Reducing the risk of breakdowns Improved operational reliability.
- Increases the level of planning of maintenance activities.
- Professional development of staff
- Reduced maintenance costs
Disadvantages
- Cost of unnecessary spare parts and labour time
- Risk of excessive maintenance of machinery
- Costs of unnecessary downtime
- Often static maintenance planning with limited feedback of experience to the maintenance plan
Predictive Maintenance
According to the standard, predictive maintenance strives for finding the failure during its failure development time by predictions from repeated analyses or by evaluating known properties and parameters of a unit's degradation. Using today's technology, it is common to have some intelligent monitoring system that analyses and processes various measurements. This allows you, for instance, to determine when to change bearings in a unit.
In the maintenance system, we handle this by connecting wireless sensors directly via "plug and play" to measure, for example, temperature, pressure or humidity. Through a simple configuration, you set a trigger for when you want to create a work order with an appropriate instruction for what to check or perform.
Condition checks can also be done by visual inspections or collecting data, those are then analysed and decisions are made on planned and Predictive maintenance. This can be scheduled inspections and collecting data by operators or maintenance personnel. The goal of predictive maintenance is to reduce downtime and to predict when it is time to replace a device, for example, at an optimised time to take advantage of its full lifespan.
Advantages
- Minimising downtime and increase planning efficiency.
- Reduction of service and material costs.
- Extends the use of components and machines.
- Status-based maintenance replaces time-based maintenance.
- Reduced maintenance costs.
Disadvantages
- May increas initial costs.
Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous (Operator) maintenance aims to increase the operational reliability of production equipment by establishing close cooperation between maintenance technicians and operators. Operators have a unique insight and knowledge of daily operations that is very valuable for maintenance. At the same time, maintenance has unique understanding of care and function. By exchanging and transferring knowledge closer to the equipment, unwanted variations can be detected and corrected before faults occur. Maintenance technicians have a very important role as supervisors, teachers and coaches in this work.
Involving operators in the execution of certain maintenance actions also provides more opportunities for daily supervision and weekly maintenance. Examples of maintenance actions that can be carried out by operators includes checks, lubrication, replacements and simple repairs.
Autonomous maintenance will eventually also free up time for maintenance staff to work more on improvement maintenance, such as specialised maintenance and improvements to increase operational reliability.
Production should be responsible for ensuring that the planned autonomous maintenance is carried out according to the applicable procedures and intervals and that the work is reported according to instructions. If a deviation is detected during an inspection, this is handled via a follow-up job in the maintenance system.
Maintmaster Maintenance Manual
This free manual can be used as a practical guide and support in the daily maintenance work and as part of the introductory material for newly employed personnel.
In this manual, you will learn:
How to create vision, strategy and policies for your maintenance team
How to build a maintenance team
Which KPIs to use and how to set them up
How to base your work on the EN Maintenance Standard
And a lot more…
- 1. Maintenance according to Euorpean standards
- 2. Maintenance Vision, Strategy & Policy
- 3. Maintenance standard
- 4. Preventive Maintenance
- 5. Corrective Maintenance
- 6. Improvement Maintenance
- 7. Modification
- 8. Case Management
- 9. Organisation
- 10. Finance
- 11. Goals & Key Performance Indiscators (KPIS)
- 12. Implementation in MaintMaster
- 13. Planning & Scheduling
- 14. Spare Parts Management
- 15. LEAN - 5S
- 16. Systematic Work Environment Management
- 17. Learn the basics of a CMMS
