Chapter 12
Implementation in Maintmaster CMMS
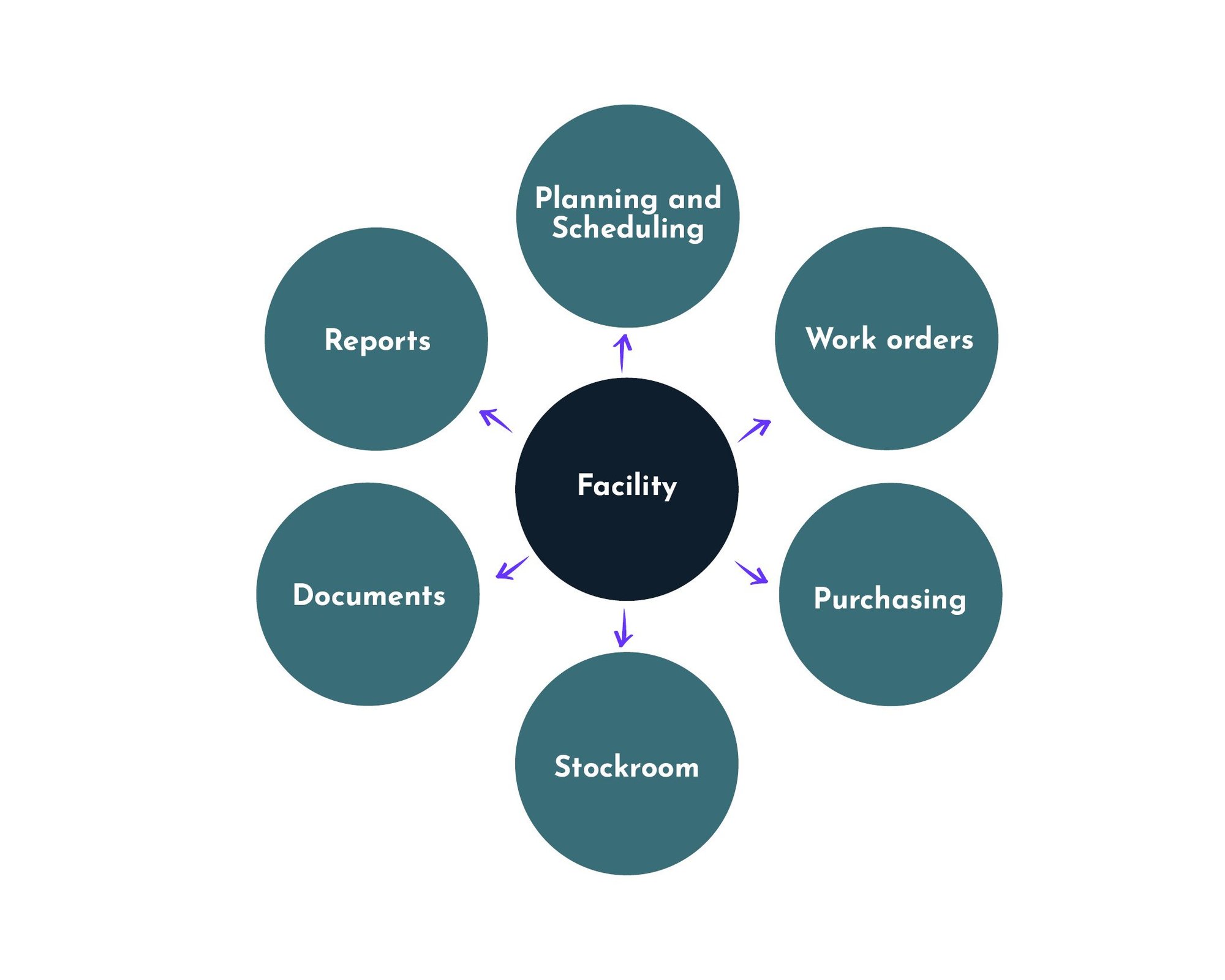
Why do you need a maintenance system?
The management and planning of maintenance requires a systematic approach. The information that can be collected in a maintenance system provides invaluable support in planning and executing all types of maintenance activities, and helps to ensure operational reliability. Regardless of the strategy, some form of preventive maintenance is always required, and for this to work documentation, planning and follow-up are required to get the intended return on investment. A maintenance system is also the hub for all the information a maintenance technician or planner needs. What has been done previously, which spare parts are suitable, have we carried out inspections according to routine, what deviations have we found?
In MaintMaster, job categories and completion codes are customised according to standard EN 13306. This enables easy monitoring and value-adding decision-making.
Maintenance according to european standard
In order to make correct analyses, it is necessary that the staff reports in the same way and that they understand what the different definitions mean in the maintenance system. MaintMaster CMMS is adapted to the EN 13306 Terminology for maintenance, where it is clear what the different terms mean. The following pages show different terms and concepts in the standard with an explanatory text, and how this is implemented in MaintMaster.
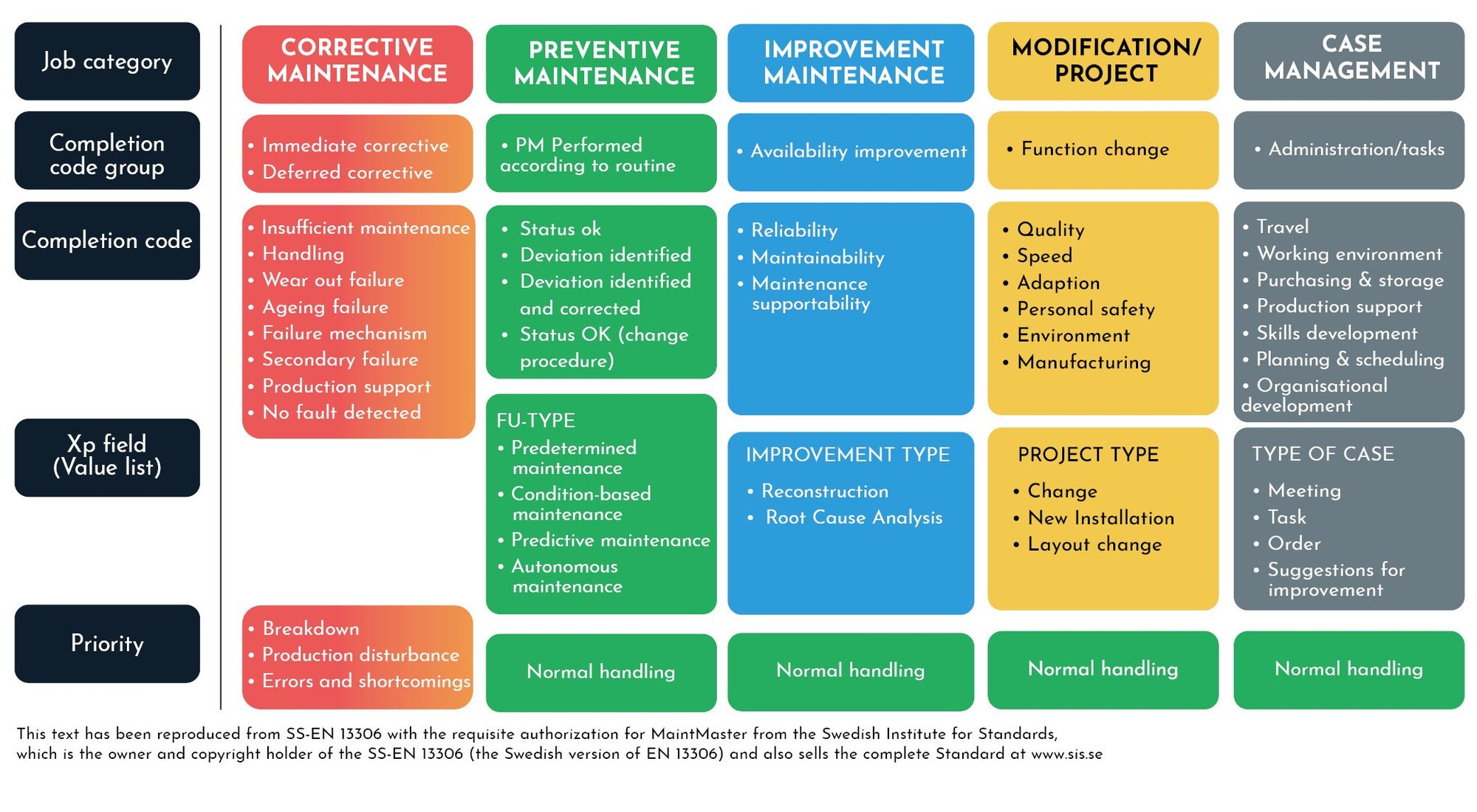
Job categories, completion code groups and completion codes in MaintMaster based on standard EN 13306
Completion code groups: Corrective maintenance
Completion code group: Immediate corrective maintenance
Maintenance performed immediately after a defect has
been detected in order to avoid unacceptable consequences.
The machine is down, fix now! Downtime must always be specified before completion with this completion code group.
Completion code group: Deferred corrective maintenance
Corrective maintenance that is not carried out immediately after the detection of a malfunction but is deferred in accordance with the given maintenance directives.
The machine works, but not very well. The job can be scheduled for a later date.
Always strive to move actions from unplanned to planned maintenance activities. Initially, this is the fastest way to achieve higher reliability and more efficient maintenance work.
Completion codes for completion code group: Immediate and deferred corrective maintenance.
The following completion codes are used in this example to indicate the reason why an error has occurred.
Insufficient maintenance
Defects arising from improper or unperformed maintenance.
Handling
Errors resulting from improper handling of equipment or machinery.
Wear out failure
Faults whose probability of occurrence increases with the operating time or the number of completed work cycles or the load to which a unit is subjected.
Ageing failure
Faults whose probability of occurrence increases with time. This time is independent of the operating time of the unit.
Failure mechanism
Physical, chemical or other process that leads to, or has led to failure. e.g. design failure, incorrect choice of materials or method failure.
Secondary failure
Failure of a unit directly or indirectly caused by the failure
of another unit, e.g. power failure, loss of compressed air, etc.
Production support
Used for reporting support services to production that are not directly maintenance related, such as assistance with changeover or machine start-up.
No fault detected
Completion code for those occasions when no fault can be found. Can be used, for example, when a "loose contact" is suspected and when restarting or resetting equipment.
The error cannot be recreated.
Completion code group and completion codes: Preventive maintenance
Completion code group: PM Performed according to routine
All maintenance activities regarding preventive maintenance are completed with the completion code group "PM Performed according to routine", followed by one of the following completion codes to facilitate the follow-up of completed PM activities.
Status OK
Action or inspection is carried out according to plan/ instruction, and the equipment is in a satisfactory condition and authorised for continued use.
Deviation identified
Control is carried out according to instructions and deviation is identified. Deviation management is planned and managed via follow-up jobs.
Deviation identified and corrected
Control is carried out according to instructions and a minor deviation is identified. Minor non-conformities can be addressed directly without a follow-up job, as the follow-up of these actions does not add much value.
Status OK (change procedure)
The equipment is in good condition and approved for continued use but the routine or intervals need to be adjusted in the original job.
Property to indicate the type of Preventive maintenance
It is easy to specify different types of preventive maintenance in MaintMaster. It is equally easy to create reports showing what has been performed. This is done by using an extra property on the job category Preventive Maintenance, containing a valuelist/dropdown with captions as shown below.
-
Create a Property in MaintMaster, data type Value list, with the name type of PM action. Enter the following captions as optional values.
Predetermined maintenance
Preventive maintenance carried out at specified intervals or after a specified use without regarding condition.
Condition-based maintenance
Preventive maintenance which consists of checking and monitoring the condition of a unit in terms of its operation and characteristics.
Predictive maintenance
Maintenance action following a condition-based maintenance, when a prediction of a unit's deteriorating performance based on analysis and evaluation of key characteristics is made.
Operator maintenance
Maintenance carried out by the user or operator of the machinery
Completion code group and completion codes: Improvement maintenance
Completion code group: Availability improvement
The following completion codes are used to indicate the purpose of the improvement work.
Reliability
Ability of a unit to perform the required function under given conditions during a specified time interval.
Maintainability
The ability of a unit, operating under specified conditions, to be maintained in, or restored to, a state capable of performing the required function when maintenance
is performed under specified conditions and using established procedures and resources.
Maintenance supportability Completion code group: Function change
The ability of the maintenance organisation to provide the right maintenance resources at the required location, to perform required maintenance actions on a unit, at a specified time or during a specified time interval.
Completion code group and completion codes: Modification
Completion code group: Function change
The following completion codes are used for completion of cases where the purpose has been personal safety improvements, cycle time or quality improvements of the product.
Alternative modification of machine for a new product, packaging or environmental measures.
Quality
For reporting back an action where the purpose is or has been to improve the quality output of a machine or equipment.
Speed
For reporting back on an action where the purpose is or has been to improve the speed or cycle time of a machine or equipment.
Adaptation
Used to report back an adaptation or adjustment of a piece of equipment for example for a new product or packaging.
Personal safety
Used to report back on cases where the aim is to improve personal safety. Including ergonomic improvement activities.
Environment
For reporting environmental improvement cases.
Manufacturing
Manufacture of new machinery, tools or spare parts.
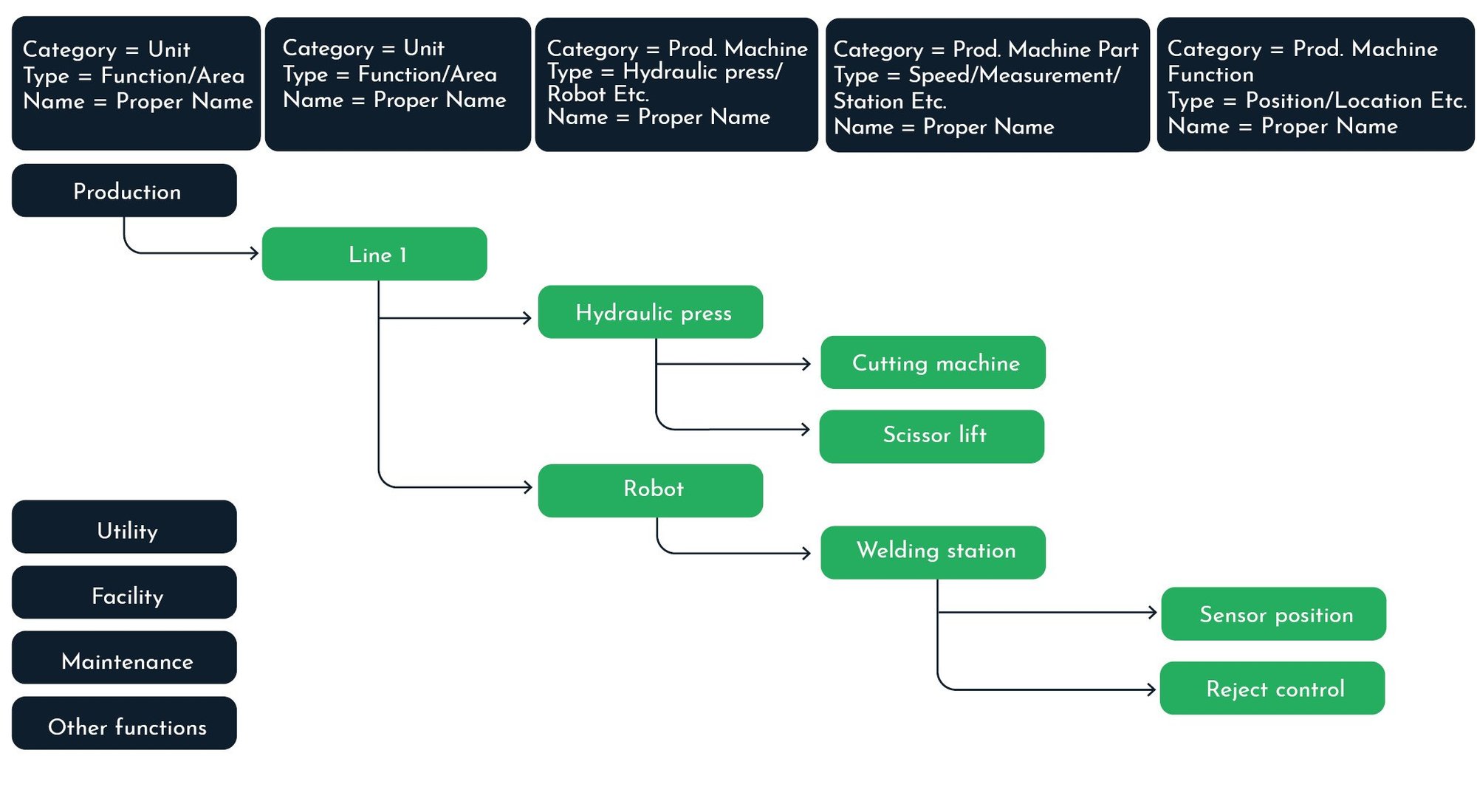
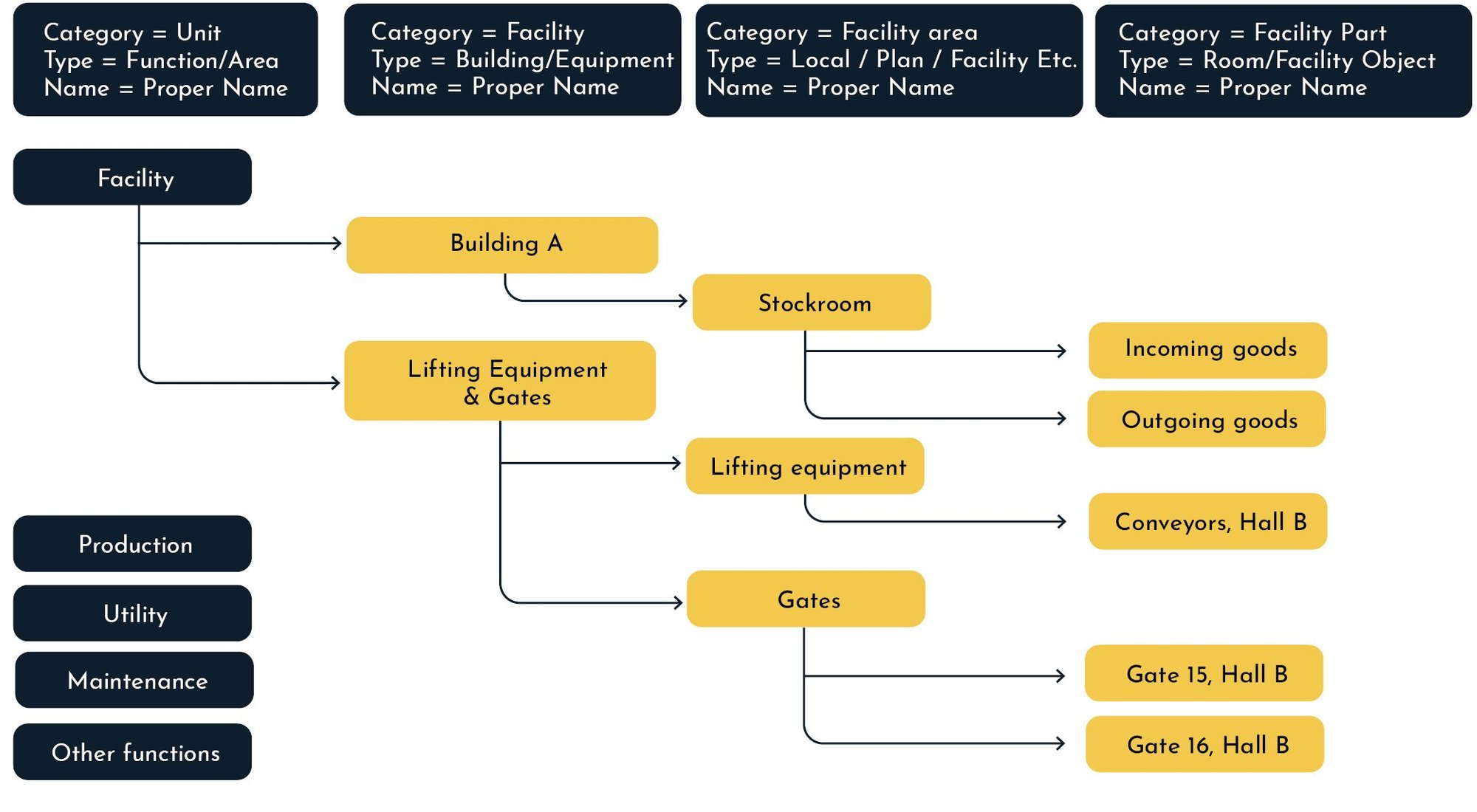
Build your site explorer: Production (green icons)
Build your site explorer: Facility (yellow icons)
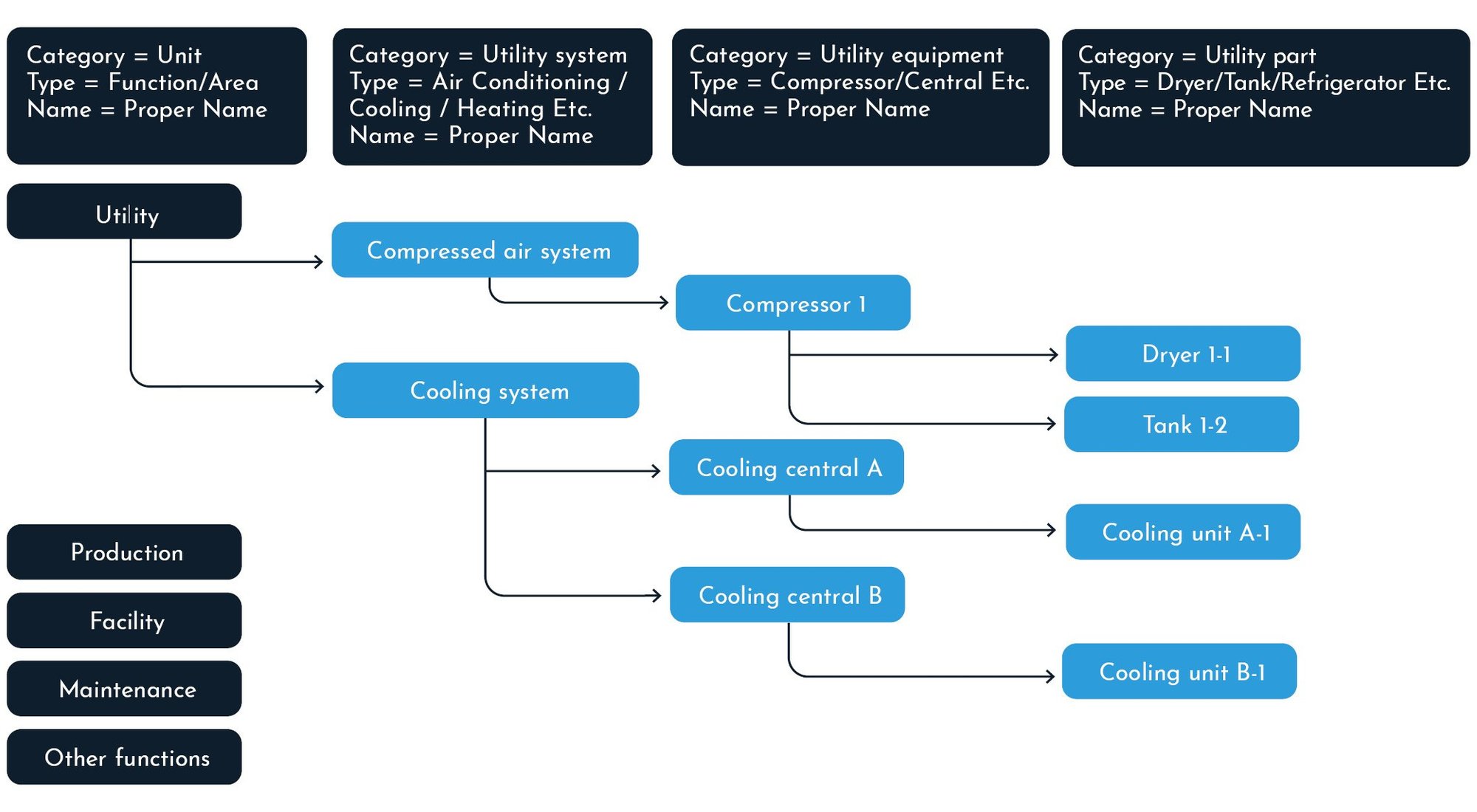
Build your site explorer: Utility (blue icons)
Maintmaster Maintenance Manual
This free manual can be used as a practical guide and support in the daily maintenance work and as part of the introductory material for newly employed personnel.
In this manual, you will learn:
How to create vision, strategy and policies for your maintenance team
How to build a maintenance team
Which KPIs to use and how to set them up
How to base your work on the EN Maintenance Standard
And a lot more…
- 1. Maintenance according to Euorpean standards
- 2. Maintenance Vision, Strategy & Policy
- 3. Maintenance standard
- 4. Preventive Maintenance
- 5. Corrective Maintenance
- 6. Improvement Maintenance
- 7. Modification
- 8. Case Management
- 9. Organisation
- 10. Finance
- 11. Goals & Key Performance Indiscators (KPIS)
- 12. Implementation in MaintMaster
- 13. Planning & Scheduling
- 14. Spare Parts Management
- 15. LEAN - 5S
- 16. Systematic Work Environment Management
- 17. Learn the basics of a CMMS